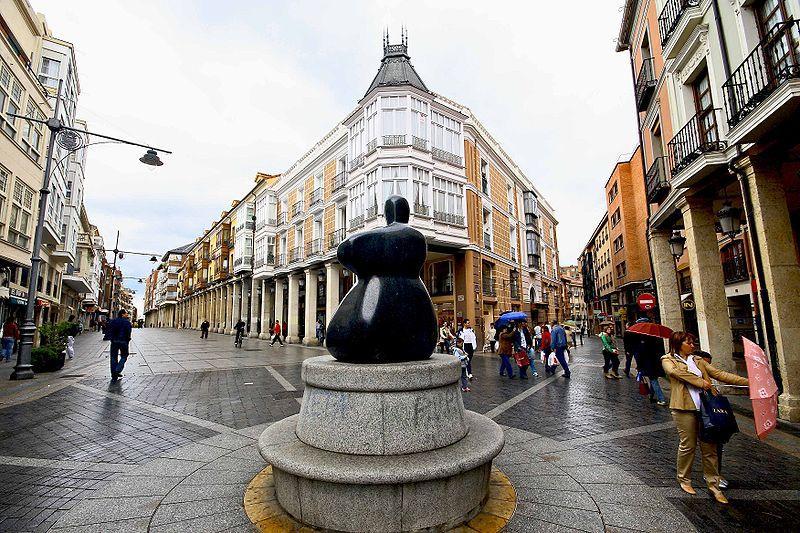
Palencia, Castela e Leão, Spain
Suggest Place to Visit
3673
Track to location with GPS |
 |
Old age
The historical origins of the city remain uncertain, but what there is archaeological evidence is pre-Roman settlements on the site of the current city, which the Celtiberians called Pallantia. The town that occupied it was the Vacceos: the most cultured of the Celtiberian tribes, agrarian and with a powerful military organization.
The only trace of Romanization that remains in the city is Puentecillas, whose primitive Roman origin has been remodeled several times. This bridge allowed access to the island of Sotillo de los Canónigos, whose Bolo de la Paciencia was the city's lieutenant. It was restored and remodeled in the Middle Ages.
With the Visigoths came one of the most splendid stages for the city, since they made it the seat of the court, in addition to that since the fourth century it was also a prominent episcopal seat (it is said that their diocese was the most important in Spain after the Toledana). There are remains of the Visigothic vestige in the Crypt of San Antolín (which is the current crypt of the Cathedral) and in the nearby town of Baños de Cerrato with its church of San Juan de Baños (7th century), located just 7 km from the capital that is considered the masterpiece of Visigothic architecture.
Middle Ages
It was developed as a city during the reconquest by the Asturian kings. The Middle Ages is the most turbulent period in the history of the city, but also the one with the greatest projection in the events in the history of the Kingdom of León and the Kingdom of Castile.
Alfonso VIII of Castilla was the most determined promoter of the city, granting it charters and the first free council, and establishing between the years 1208 and 1212, at the request of Bishop Tello Téllez de Meneses, an educational institution that was the first University of Spain called University of Palencia or General Study of Palencia, receiving the pontifical approval of Honorius III in 1221 and disappearing a few decades later.
He fought nobly in the Battle of Las Navas de Tolosa, in 1212, which led to the award of various assets.
It is also noteworthy that, in 1388, while the Palencians were out of the city, troops of the Duke of Lancaster arrived with the intention of looting the city, which was courageously defended by the Palencian women, preventing Lancaster from subduing Palencia. For this reason, the woman from Palencia was awarded the yellow band of honor, which only men could wear, and which today is evident in the regional costume.
It is in the fourteenth century when the importance and volume that the city had acquired forced the construction of a new cathedral capable of satisfying the needs of a thriving population. The building was built on the ruins of the previous Romanesque style, and in turn on the previous ones of the Visigoth cathedral, all of which remain in the current building. Although the first stone of the new cathedral was laid in 1321, the works did not ´´complete´´ until the end of the 16th century. It is said "concluded" because this great temple is not finished since it is believed that there would be a further chapel to be built, the renovation of the tower and perhaps the construction of two towers on the main façade as was customary at the time.
Modern age
The economic prosperity of the 16th century made Palencia, along with the other Castilian provinces, the economic and demographic heart of the Spanish Empire. The most beneficial event for the life of the city during the 18th century was the construction of the Canal de Castilla by Carlos III of Spain, one of the greatest engineering works of the time in Europe. During the Modern Age, the great churches that Palencia has today were built, such as the Compañía, San Pablo, Las Claras, and San Francisco in Gothic and Renaissance styles.
Contemporary age
Twentieth century
The 20th century was one of great prosperity for the city:
The wars of the 20th century, such as World War I or the Spanish Civil War, favored, to a certain extent, the economic development of the city, whose industries (flour, wool and weapons) were essential to supply the belligerents. At present, it is above all a city of services, although the automobile and auxiliary, agri-food and construction materials industries are of great importance.
The remodeling of the city led to the creation of a multitude of green spaces such as the Carcavilla Park or the Isla dos Aguas, which led the city to be the first in gardens in Spain per inhabitant.
The appearance of the great geniuses of the Palencia arts such as the sculptor Victorio Macho with his famous Cristo del Otero and his Monument to Berruguete or the architect Jerónimo Arroyo who decorated the city with many buildings and palaces such as the Provincial Council, the Villandrando School, the IES Jorge Manrique or the current Health Center of La Puebla.
Civil war
In Palencia capital the majority party and with greater force was the Socialist Party while in the province the most important party was Agrarian Popular Action. The Spanish Falange had very few members, most of them in jail.
On July 19, 1936, a military column left for Venta de Baños, which took the train station and, immediately afterwards, the entire city without hardly anyone noticing it. At seven in the morning, another force left for the center of the provincial capital to declare a state of war and occupy the most important buildings. Contrary to that in Venta de Baños there was strong resistance, there were shootings in the streets and great resistance in the Republican Civil Government for two hours in charge of Assault Guards and Carabineros concentrated by the Governor, López Muñiz, who later was shot dead. when he had already been arrested. The Provincial Council, the Town Hall and the train station were more easily occupied. General Ferrer de Miguel took over the Provincial Council and the Civil Government, although for a few days from July 19 they were occupied by another military man. As mayor was an artillery captain.
Many men were arrested on the 19th in the capital Palencia when they arrived armed from their towns, responding to the summons that the Civil Governor had made the night before. For his part, the head of the Palencia Falange, was released and quickly organized a mixed squad of Falangists and civil guards that toured the towns of the province eliminating all kinds of resistance.
Palencia is a Spanish city in the community of Castilla y León, capital of the province of the same name located in the Tierra de Campos plain, on the bank of the Carrión River. Located at an altitude of 749 m, it is 235 km from Madrid, the national capital, and in 2008 it had 82,626 inhabitants over an area of 94.71 km². It is an important industrial center of Castilla y León, since it employs 3,344 workers in the sector.
Geography
The city of Palencia is located in inland semi-humid Spain, specifically in the northern part of the northern sub-plateau. It is located in the valley of the Carrión River near its mouth in the Pisuerga River, the first one that crosses the city from north to south forms four islands, two large: Dos Aguas Island and Sotillo Island and two others of one size reduced, the river (with a medium and constant flow generally throughout the year) opens into three branches when entering the city, forming the island of Sotillo and another small island, both occupied by a park called El Sotillo de los Canónigos.
The river joins again (it is the place where the Puente Mayor (16th century) is located and then it opens into two arms, forming the largest island (Isla Dos Aguas) which in its northern area has a large park and the South area, sporting and with a golf course. At the end of this island the other small islet is formed. The Carrión River is also the source of the small waterfalls it has and the recently created artificial geyser. On the outskirts of Palencia the river joins again.The flat city has two hills in the northeastern part, in the one closest to the city center is the colossal image of the Heart of Jesus of Palencia, the Christ of the Otero that dominates the city.
Palencia has a mountain with 1,438 hectares of oaks and holm oaks 6 km away and 865 meters above sea level. The people of Palencia call it ´´El Monte el Viejo´´. The mountain, which is one of the places of recreation and leisure for the population, is accessible by a road and a bike path. The vegetation is formed in the highest and driest part of holm oaks and some oak and as one descends in altitude the vegetation turns greener, to oaks and poplars. In the mountain there is a large fence in which native deer inhabit which can be fed with luck by the passing visitors themselves. In addition to the hunting reserve, Monte el Viejo has several facilities: for exercising (simple) and for athletes (more complex), the municipal swimming pools of Monte, a bar and a restaurant, a refuge and the so-called Little House and Big House, the last one is a 16th century inn.
In the outskirts of the city, crops dotted with groves of poplars, oaks and holm oaks are the most abundant vegetation.
Palencia is not crossed by the Canal de Castilla, but a foothill called the Dársena del Canal does enter the outskirts of the city. This dock was used to load goods but the arrival of the railroad left it in disuse. Currently it is thought to condition it as a tourist attraction.
The municipal term of Palencia also includes the locality of Paredes de Monte.
Location
The city of Palencia is located in the northeast of the Iberian Peninsula, on the Northern Plateau. The Parque del Salón de Isabel II, the geographic center of the city, is located at the coordinates: 42º00'23 North latitude and 4º31'45 West longitude. It is located 749 meters above sea level.
Hydrography
The town is crossed by the Carrión River, to the east is most of the city while to the west is the Allende del Rio neighborhood. In addition, the municipal term is crossed by the Canal de Castilla, by the Villalobón stream and other ditches. On the outskirts of Palencia there is one of the docks of the Canal de Castilla for access to which the "Ramalillo" of Palencia was built, more than 1 kilometer long.
Orography
Palencia is located in a plain, surrounded by several mountains: mount ´´El Chivo´´ and mount ´´El Viejo´´.
Mount ´´El Viejo´´
It is a large mountain that is located about 6 kilometers from the town center, where you can enjoy free time and a large number of leisure activities (it has various circuits, swimming pools ...). In 1191 it was sold by King Alfonso VIII to the City. It has various places and enclaves such as Vallejuelos, Cigarral and Buentrigo, with a great variety of animal and plant species and those of Valle de San Juan or the Little House with panoramic views. In the Casa Grande you will find hotel facilities in a building built in the 16th century. El Refugio is one of the most popular areas that has a restaurant, circuits, and is located near the deer reserve park, with an abundance of animals.
Weather
Its interior character, away from almost any maritime influence, determines that the climate is continentalized Mediterranean, slightly oceanized due to its relative proximity to the Cantabrian Sea and that in the western part of Castilla y León (the place from which the Atlantic clouds come) there is no there are mountains to stop cloudy fronts.
It has a wide thermal oscillation. The temperatures are particularly cool due to its surrounding relief, being one of the coldest capitals in Spain. The average temperature in January is just over 3.3 ° C and that of July is 21 ° C, but there are historical absolute minimums of up to 14 ° C below zero and up to two or three months of frost. In summer the temperature rarely reaches 40 ° C.
Annual rainfall is scarce with an average of 414.2 mm, with a spring maximum and a summer minimum. Clear days are 85 as an annual average.
The year 2007 had the lowest average temperature and the most abundant rainfall in the last decade, and January 2009 was the coldest in the last 10 years.
Parties
The Baptism of the Child: On January 1, of Regional Tourist Interest. Singular festival that is celebrated around the Church of San Miguel with a procession and a ´´stone´´ of candies and candies.
San Antón: It is celebrated on January 17 in the vicinity of the Church of San Miguel where the animals of the attendees are blessed.
Virgin of the Street Festival (Las Candelas): February 2. Patron saint of the city. In the parish of La Virgen de la Calle the image of the Virgin known as ´´La Morenilla´´ is venerated and it is carried in procession to the Cathedral, before the fervor of the faithful.
Easter: March-April, (first spring full moon) is the most important festival in the Palencia calendar as it has the distinctive National Tourist Interest festival. The processions of ´´La Borriquilla´´, ´´Oración del Huerto´´, ´´Los Pasos´´ and ´´Santo Entierro´´ are of relevant importance. See: Easter in Palencia.
Pilgrimage of Santo Toribio: The Sunday closest to April 16, Festival of Regional Tourist Interest. A 'stone' of bread and cheese is held at the foot of Cristo del Otero. (See Cristo del Otero)
Caracolada de San Marcos: Held on April 25 on the island of Sotillo de los Canónigos.
Girl Fair: Days around Pentecost. Popular festival in Palencia called ´´chica´´ for being the second in importance when compared to the San Antolín fairs.
Corpus Christi procession and mass: Sunday closest to Corpus Christi Thursday. The procession and mass are organized by the Penitential Brotherhood of the Holy Sepulcher and the Cathedral Chapter. The Santísimo procession in the Triumphant Chariot, of singular beauty.
San Juan's Day (colloquially ´´San Juanillo´´: June 24. Copatron of Palencia, there is a procession in which the Saint John of the brotherhood of the Holy Sepulcher parades. From its headquarters it reaches the Plaza Mayor where it is performed The traditional thyme spread The procession reaches the San Juanillo neighborhood where the relic is worshiped and a prayer is heard, at night the Bonfire of San Juan takes place.
Festivities of San Antolín: Patron of Palencia, September 2 and surroundings. Processions, parades, bullfights, proclamations and parades of peñas follow one another. It is the main festival of Palencia.
Procession in honor of San Francisco: After mass, the brotherhood of San Francisco (better known as Santo Sepulcro) carries out a small parade with the image of the Saint.
Music
In the capital of Palencia several musical events are held each year such as:
Get hooked on music: Festival organized by the (40 Principales) and Cadena Ser, and with the sponsorship of the City Council of Palencia and the Junta de Castilla y León, on the end of the classes before the Christmas holidays.
It is an initiative that tries to avoid the sedentary life of young people, as well as the consumption of alcohol and other drugs. In its 13 editions it has featured national artists such as Álex Ubago, David DeMaría, Ragdog and Los Caños, among others. It takes place at the Marta Domínguez Municipal Pavilion and is free to attend.
´´Ahora´´ Festival: It is a contest, organized by the Junta de Castilla y León together with the Cultural Association for the Promotion of Creative Music and the City Council of Palencia.
Groups and artists with different trends perform and whose performances will be exclusive in our country. Initially it was held in the Carabel room, but in the last edition the situation was changed to the Principal Theater.
Festival ´´Música Futura´´: It takes place in the Municipal Pavilion and has regional groups that seek opportunities on the national scene.
Independent Festival of Palencia: Festival that features alternative music bands from the country such as Sidonie or Second.
Palencia Sonora: Rock Festival that usually coincides with the Feria Chica in which groups such as Sidonie, Standstill, Standar, Cooper, Macaco, Sugarless, Vetusta Morla and the Palencians La Familia Iskariote, among others, have participated.
Jazz and Folk Festival: It coincides with the Feria Chica and so far there have been three editions.
Vegetation
The Palencia countryside looks green from October to June, being altered by snow and winter frost, from June or July the landscape becomes a steppe that is more reminiscent of the typical image of dry southern Castile.
The vegetation, given its situation straddling the humid Spain of the north and the dry Spain of the south, is mainly composed of poplars (a species of repopulation), oaks and holm oaks.
The city has the largest landscaped area in Spain in relation to the area it occupies and is one of the largest in Europe. (15,000,000 m² of gardens in the urban area: Parque de Isabel II, Jardinillos de la Estación, Huerta de Guadián, La Carcavilla, among others and more than 14,000,000 of ´´El Monte el Viejo´´)
The great parks of Palencia
According to the City Council of the capital, Palencia is the city with the most green areas per inhabitant in Spain and occupies one of the first places in the European Union. This, coupled with the low density of road traffic, makes the air in the city quite clean. The main parks of the city are:
Isabel II Room (normally called ´´The Room´´)
Huerta de Guadián (known simply as ´´Huerta Guadián´´)
Jardinillos de la Estación (known simply as ´´Jardinillos´´)
Dos Aguas Island Park
Sotillo de los Canónigos
Bishop's Gardens
Carcavilla
Ribera Sur Park
Comments
We don´t have yet any comments about:
Palencia
Palencia
Be the first to leave a comment as it is very important to inform other people
Outros locais a visitar
Within a radius of 20 km from:Palencia
Cathédrale San Antolín de Palencia |
| 2,8 Km |
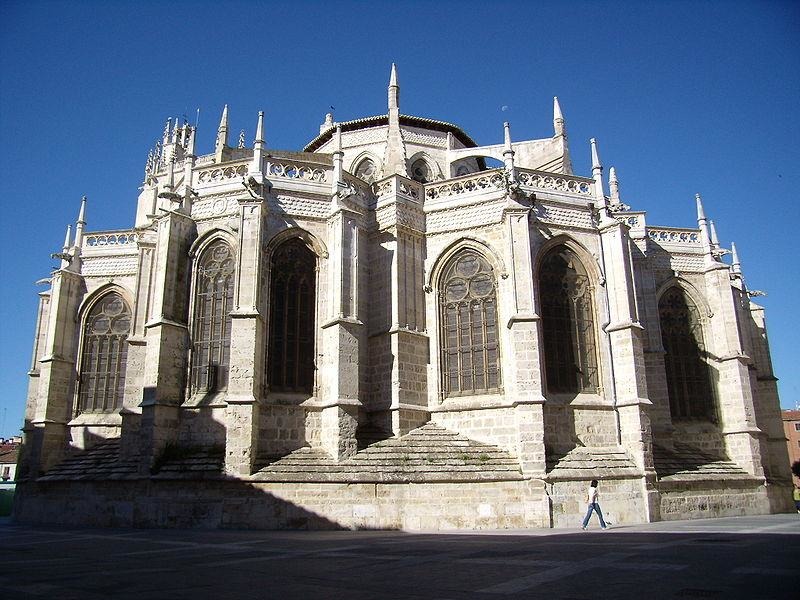 |
Château de Fuentes de Valdepero |
| 10,0 Km |
 |
Hotel reservation near Palencia within a radius of 20 km
Why to book with ROUTES TOURISTIQUES
The best prices
Our partnerships with the world´s largest operators offer research on the best market prices.
More options
At Rotas Turisticos you can book the hotel, buy the air ticket, book the transfer from the airport to the hotel and vice versa, book the local excursions, rent the car, take travel insurance and consult the places to visit and where to go.
Holiday Tips & Destinations
Hundreds of holiday destinations with all the options that allow you to easily choose the destination that best suits your dream vacation.
ROUTES TOURISTIQUES
Links